yogabook / muscles / autochthonous back muscles / multifidi
Linkmap
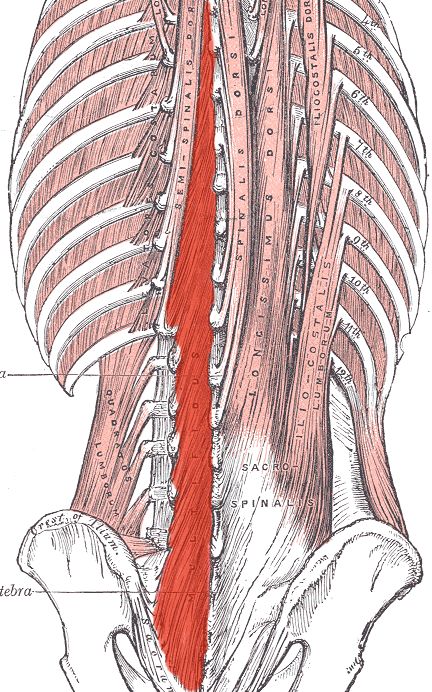
Mm. multifidi
short autochthonous back muscles running from the sacrum to the 2nd cervical vertebrae and extending over 2-5 spinal segments. The Multifidus is the most important part of the transversospinal system in the medial tract of the autochthonous back muscles. The multifidi are divided into four groups, some of which have different origins.
The Multifidus can be distinguished in three aspects:
Deep fibers: span only one segment and are important for the segmental stability of the spine.
Medium fibers: span several segments and have both a stabilizing and a movement-supporting (extensory) effect.
Superficial fibers: the longest parts are mainly extensory.
Origin:
Multifidisacrales: sacrum, ilium, local tendons,
Multifidilumbales: teat processes of the lumbar vertebrae,
Multifidithoracici: transverse processes of the thoracic vertebrae,
Multifidicervicis: transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae
Attachment: spinous processes
Innervation: medial branches of the rami posteriores of the spinal nerves
Antagonists:
Movement: Innervated on both sides: Extension of the spine; innervated on one side: Lateral flexion and rotation of the spine
Pathology: Multifidus-dysfunction, Lumbago
