Image: Rib, different views
Rib
Ribs are pairs of elongated, curved bones that span the rib cage. Due to their both ventral and articular suspension, they can be lifted ventrally-cranially for inspiration, which increases the internal volume of the ribcage and allows air to flow into the lungs attached to the ribcage from the inside.
Ventrally, ribs 1-10 are connected to the sternum directly or via cartilage, ribs 11 and 12 have no connection to the sternum and are therefore referred to as free ribs (flying ribs).
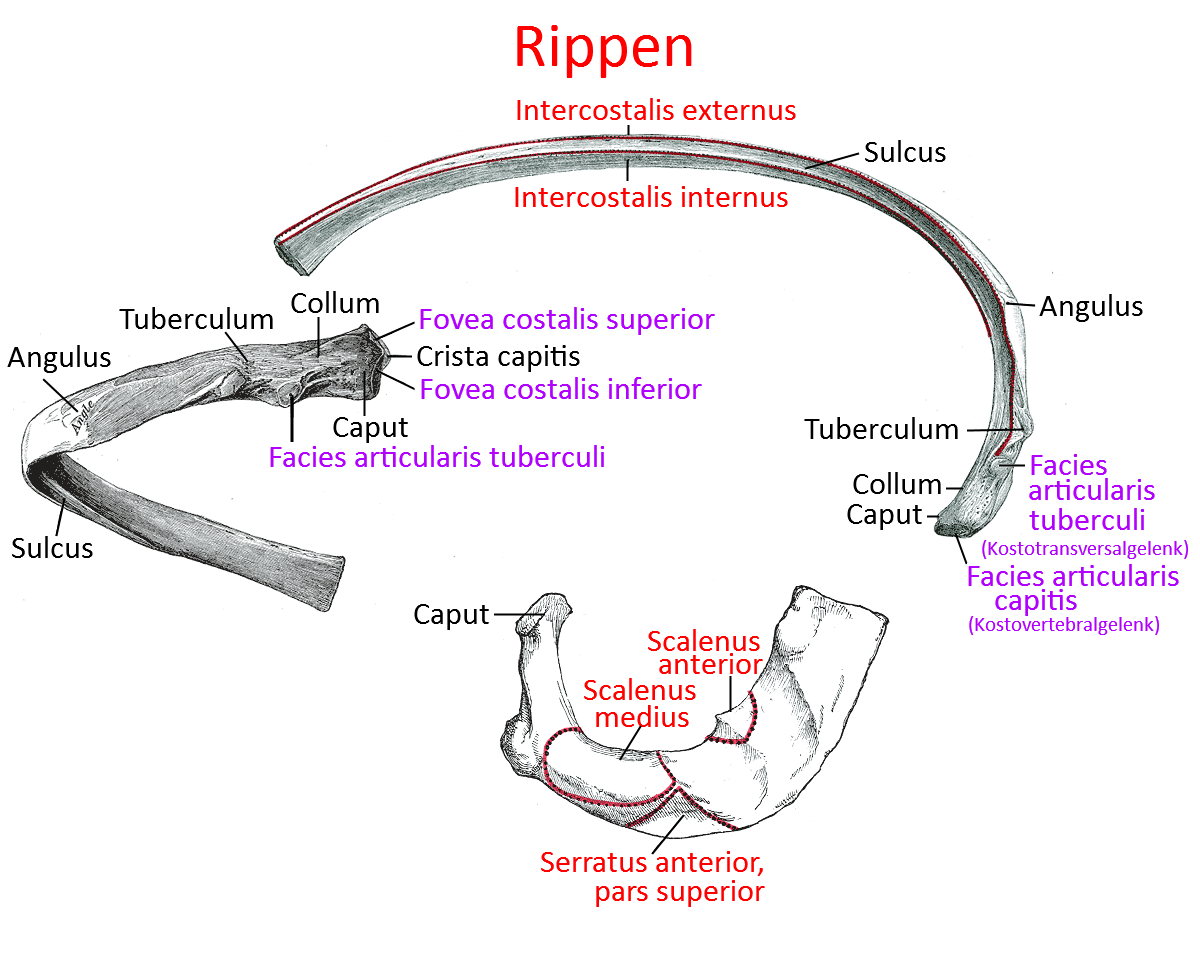
Sulcus costae
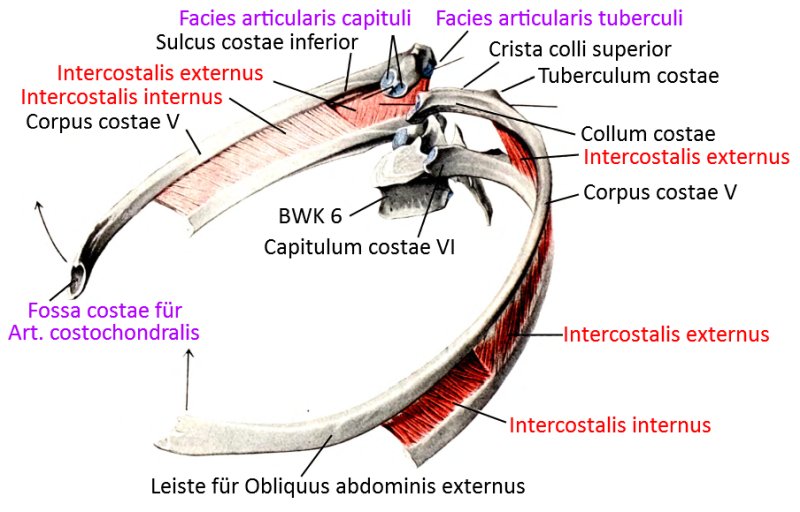
The ribs are traversed by a bone groove, within which the infracostal nerves and blood vessels run.
Angulus costae
The rib angle is the area of the rib with the greatest curvature dorsally adjacent to the costal tubercle.
Tuberculum costae
The bony tubercle on which the facies articularis tuberculi costae lies, with which the rib articulates with the transverse process of the vertebra in the articulatio costotransversarium (also: costotransverse joint), one of the two rib-vertebral joints. The other rib-vertebral joint is the articulatio capitis costae (also known as the costovertebral joint), in which the rib articulates with the vertebral body. On the vertebral body side, the vertebrae articulate with two neighboring ribs in the superior and inferior costal articular surfaces. The collum costae(neck of the ribs) lies between the two articulation surfaces of the costoververtebral and costotransverse joints. The costotransverse joints are missing in the 11th and 12th ribs, the costovertebral joints have only one chamber (and fovea).
Collum costae
The neck of the rib lying between the two dorsal articular surfaces of the rib and the vertebra.
Caput costae
The head of the rib where the articular surface with the vertebral body lies.
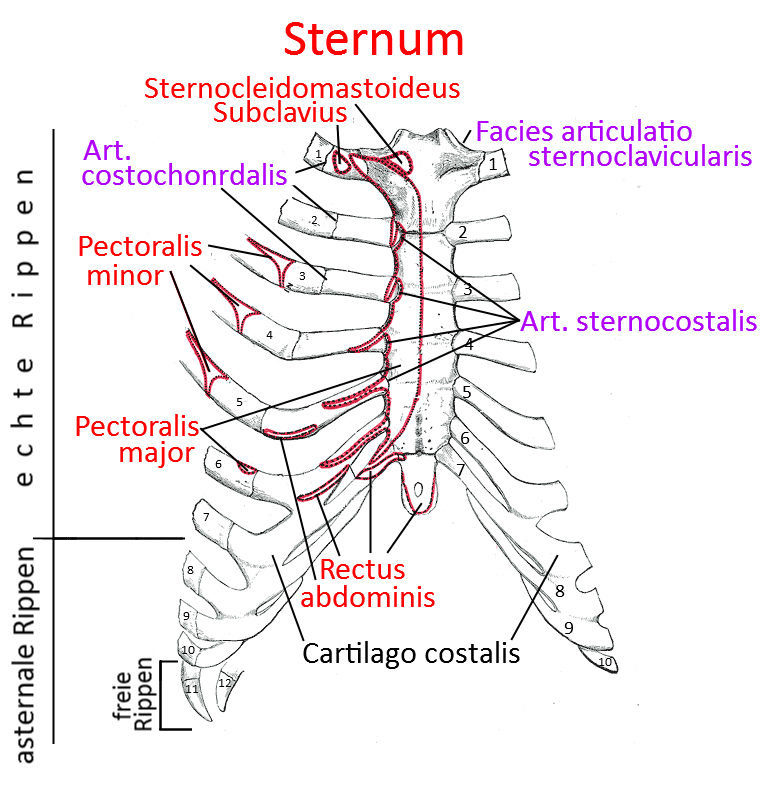
The following image shows the sternum as the ventral attachment area of the ribs.
Joints
- Costochondral joint (indirectly: sternocostal joint)
- Costovertebral joint
Images
Sternum, sternocostal joint, costochondral joint
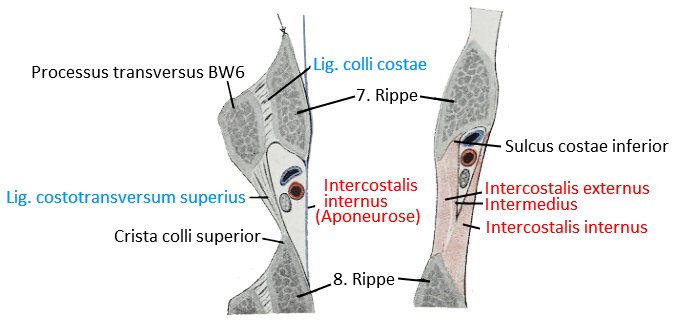
Untenstehend sind die beiden dorsalen Gelenke der Rippenbögen mit den Wirbel zu erkennen: Art. superior und Art. tuberculi costae.
Gelenkflächen für Rippen an den Wirbelkörpern

Schnitt durch zwei benachbarte Rippen
Rippen mit Interkostalmuskulatur
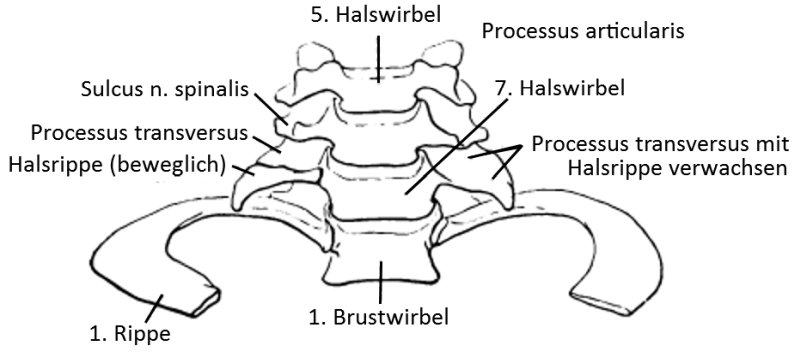
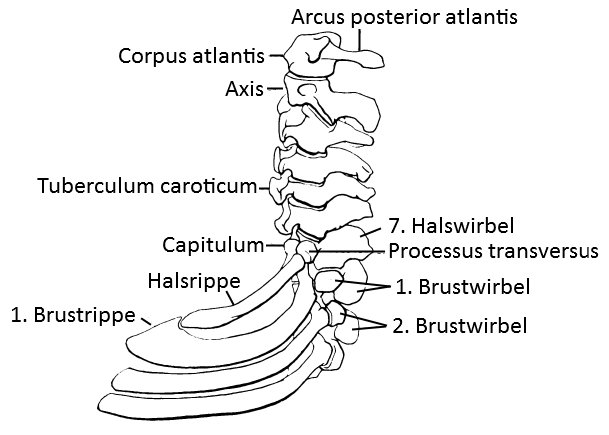
Halsrippe
Halsrippe, Rippenreste