Contents
Image: Pubic bone as part of the hip bone, next to it the ilium, ischium (Linkmap)
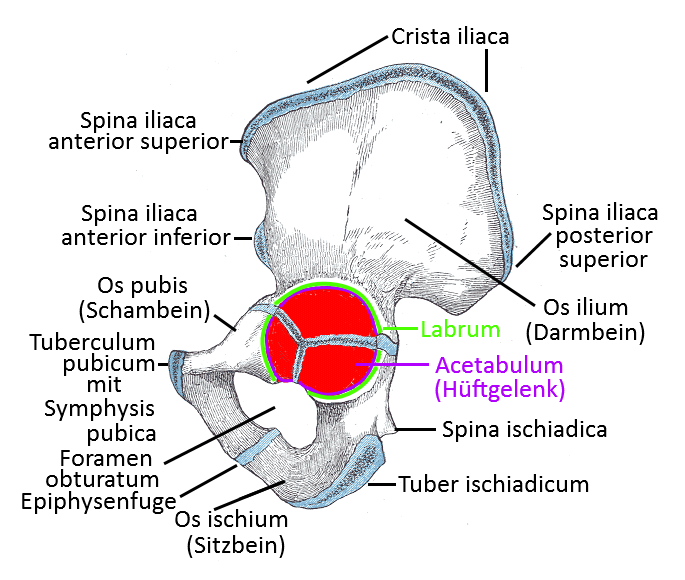
Pubic bone
The pubic bone is one of the three parts of the hip bone and the one that lies most ventrally. The ischium lies further dorsal-caudal, the ilium further cranial. The pubic bone opens ventrally into the pubic tuberosity. The pubic bone meets the ischium and the ilium in the acetabulum.
Pubic tuberosity
lat. Tuberculum pubicum, bilateral bony projections of the pubic bone (os pubis) ventrally above the genital area, i.e. the part of the pubic bone that protrudes furthest ventrally. The two pubic tubercles are connected by the symphysis(pubic symphysis), which contains an intervertebral disc, the interpubic disc, which is why it is not a true joint due to the fibrocartilaginous bone connection. During pregnancy, the discus becomes more flexible due to hormonal factors and in 1:600 cases becomes too loose. The rectus abdominis attaches to the cranial side of the pubic tuberosity.
Symphysis (pubic symphysis and ischial symphysis)
Symphysis between the left and right pubic bone with a small intervertebral disc (interpubic disc), which keeps the joint mobile.
