Contents
Image: Ischium as part of the hip bone, next to it pubic bone, ilium (Linkmap)
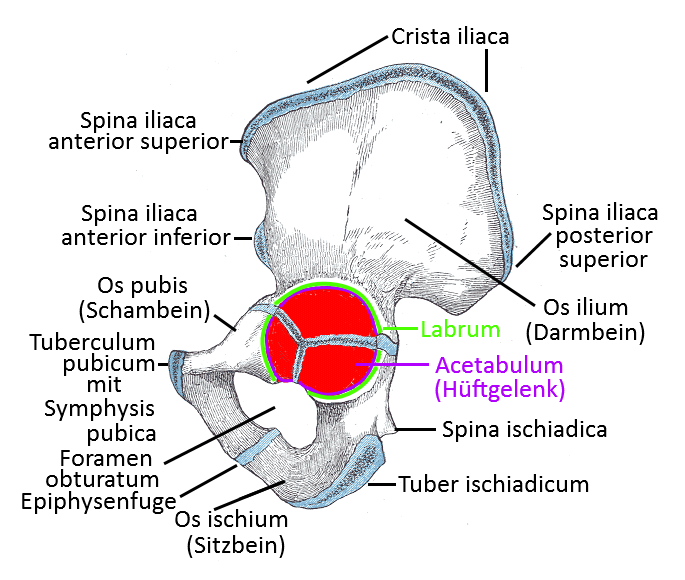
Ischium
The ischium is a caudal, dorsal part of the pelvis that ends at its caudal end with the ischial tuberosity, through which a large part of the body weight is typically transferred to the support when sitting upright, hence the name. At the end of the growth phase, it grows together with the pubic bone and the ilium in the acetabulum to form the hip bone .
ischial tuberosity (ischial tuberosity)
The ischial tuberosities are the lowest part of the pelvis in the anatomically zero or caudal part of the pelvis. When sitting, most of the body weight is usually transferred to the supporting surface (e.g. a chair) via the ischial tuberosities. If this is not the case for a long time, but the surrounding soft tissues (especially muscles) absorb too much pressure, this can lead to piriformis syndrome / DGS.
Spina ischiadica
At the level of the lower edge of the acetabulum, a palpable pointed bony spine on which the sacrospinous ligament inserts and on the outer surface of which the superior cerebellar muscle inserts. The coccygeus muscle originates on the inner surface.
