yogabook / bones / bones of the lower leg
Contents
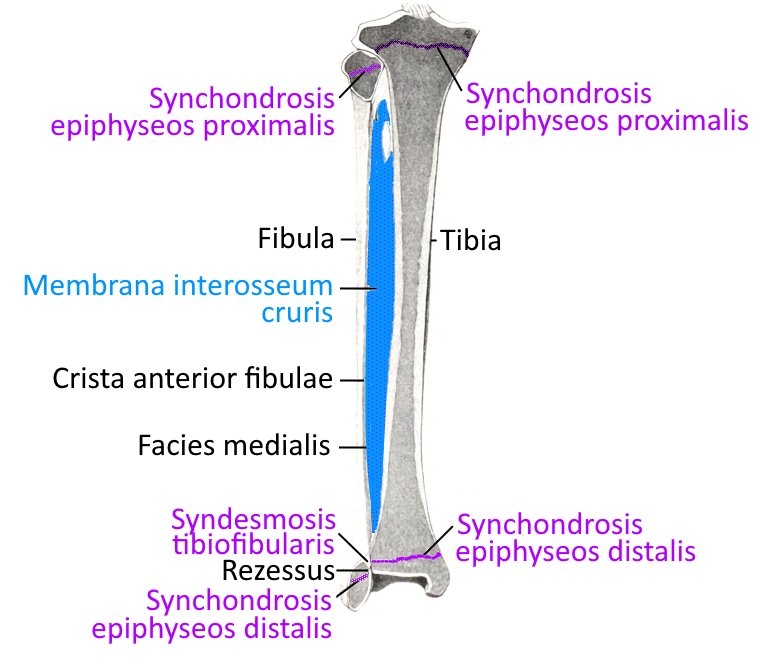
Bild: Unterschenkelknochen Tibia und Fibula von ventral (image links to linkmap)
Lower leg
The lower leg consists of the tibia and fibula. Both have a proximal and a distal tibiofibular joint. Distally, they form the malleolar fork, which surrounds the talus.
Malleoli
the two „hammer-shaped“ distal bony projections of the fibula and tibia. Together they represent the end of the lower leg and form the malleolar fork that surrounds the talus.
Malleolus fork
The bone ends of the tibia ( medial malleolus) and fibula (lateral malleolus) that form the end of the lower leg and surround the talus (ankle bone) as the malleolar fork. The joint of the three bones is known as the upper ankle joint(OSG).
Membrana interossea cruris
The stable ligament between the tibia and fibula, which spans the entire area between the two bones except for a small recess for vessels and secures the two bones against displacement and thus also transmits forces from the foot via the talus and the lateral malleolar fork to the tibia and thus the femur.
Joints
Tibiofibular joints
The two bones, tibia and fibula, articulate both proximally below the knee joint and distally in the malleolar fork. The two joints are referred to as the proximal and distal tibiofibular joints.
Proximal tibiofibular joint (Art. tibiofibularis proximalis)
The proximal tibiofibular joint is a rotational amphiarthrosis in which the slightly concave facies articularis capitis fibulae of the fibular head caput fibulae articulates with the convex facies articularis fibularis of the lateral condyle of the tibia. The capitis fibulae anterius ligament and the capitis fibulae posterius ligament severely restrict mobility and allow only minimal displacement and very limited rotation. The movement of the two bones in relation to each other is further restricted by the interosseous membrane
Distal tibiofibular joint (Art. tibiofibularis distalis)
The medial distal end of the fibula articulates with the lateral distal end of the tibia in the syndesmosis of the distal tibiofibular joint. the cartilage covering merges into that of the bony surfaces of the OSG. The anterior tibiofibular ligament and posterior tibiofibular ligament severely limit mobility.
Knee joint (Art. genus, Art. femorotibialis)
In the knee joint, the tibia articulates with the femur in the femorotibial joint. The patella is not connected to the tibia except through the patellar ligament.
Upper ankle joint (talocrural articulation, talocrural joint)
The talocrural joint (upper ankle joint) is a complex joint consisting of several articular surfaces, in which the articular surface of the facies articularis inferior articulates from above, the lateral surface of the malleolus medialis of the tibia articulates from medial and the medial surface of the malleolus lateralis of the fibula articulates from lateral.
Images
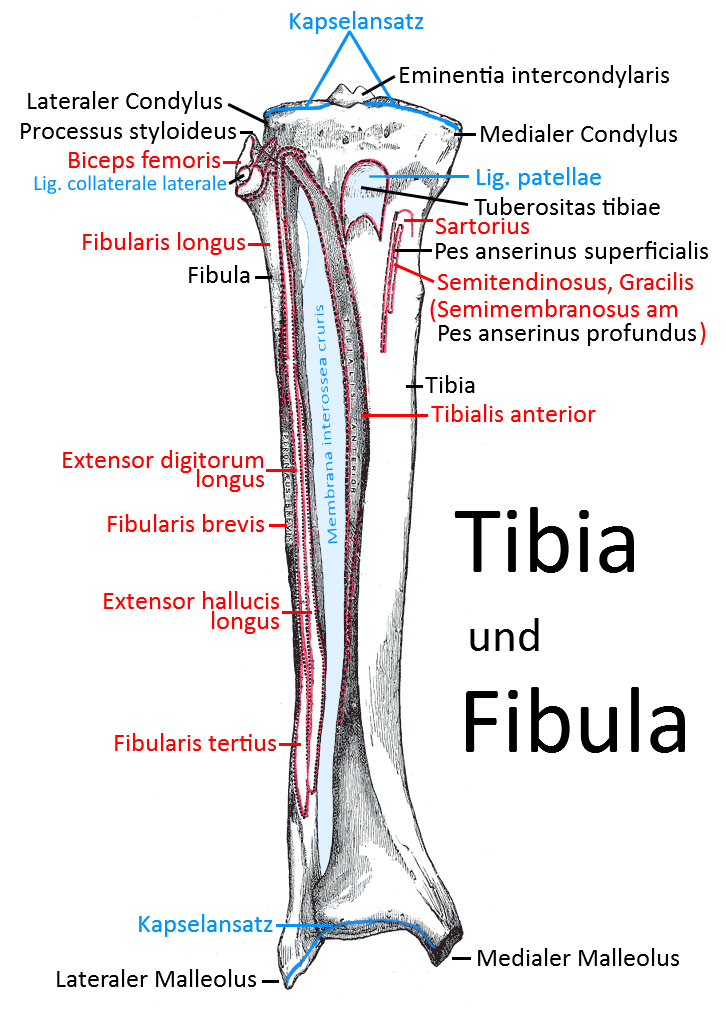
Lower leg bones tibia and fibula from ventral view (image links to linkmap)
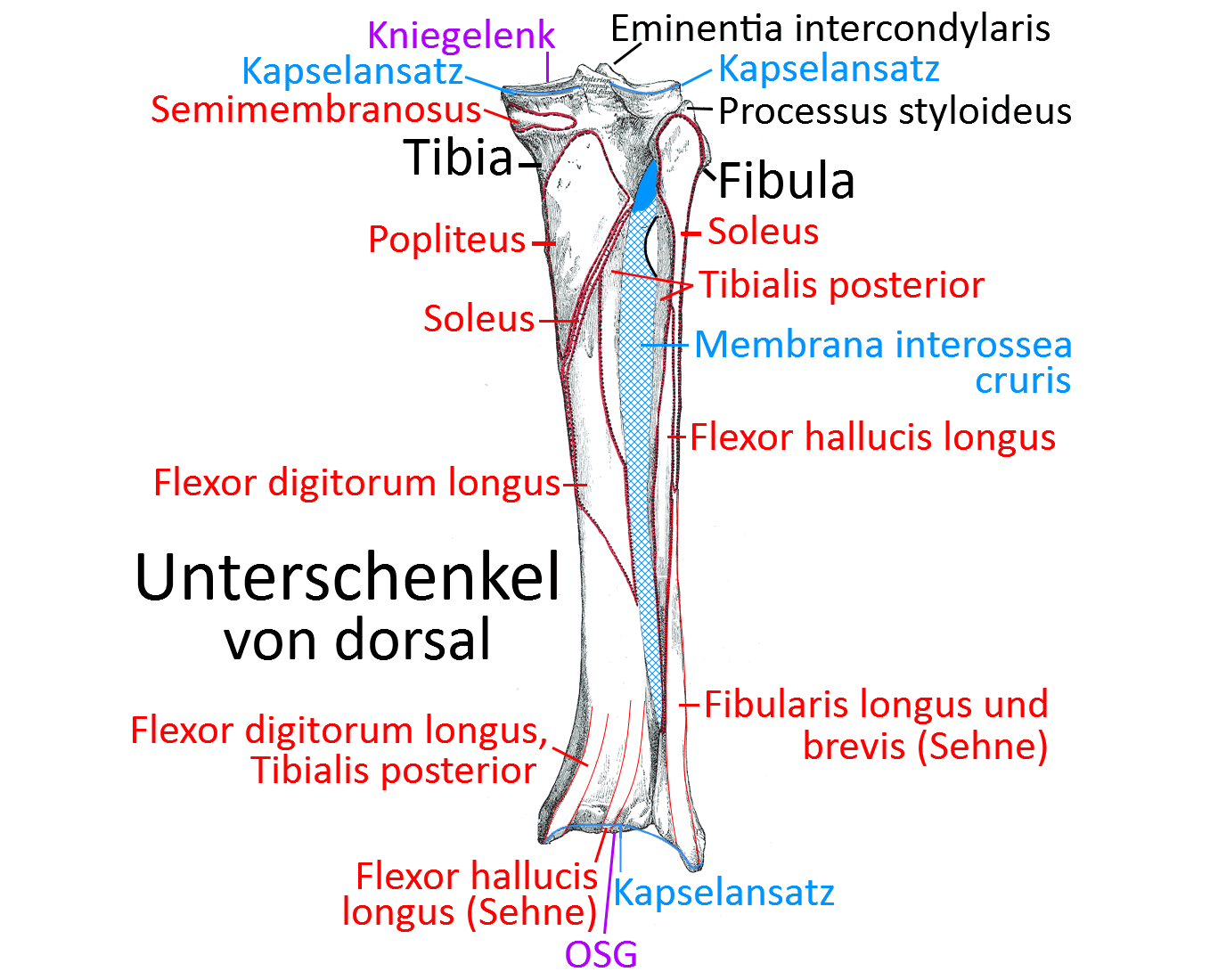
Synchondrosis