Contents
Image: Tibia from ventral (image links to linkmap)
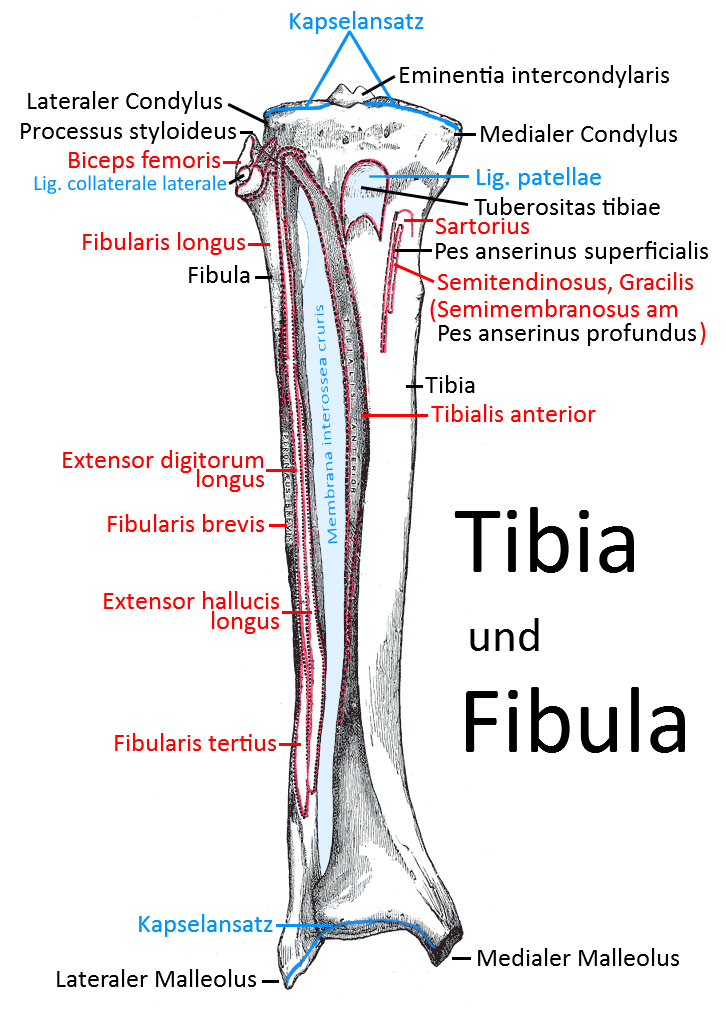
Tibia ( shin bone)
The tibia, one of the two lower leg bones. The tibia forms the knee joint proximally with the femur and the OSG distally with the talus, in which it surrounds the talus from above and medially as the medial part of the malleolar fork. The outer part of the malleolar fork, which is formed by the distal fibula, surrounds the talus laterally and above.
Caput tibiae
The head of the tibia has two condyles, the medial condyle and the lateral condyle. Both are covered with facies articularis superior, which articulate with the femur and border on the menisci.
Condylus medialis
the medial joint roller of the caput tibiae
Condylus lateralis
the lateral joint roller of the caput tibiae
Eminentia intercondylaris
The eminentia intercondylaris separates the two condyles. It forms two cusps: Tuberculum intercondylare mediale and Tuberculum intercondylare laterale
Area intercondylaris posterior
The posterior fossa, which borders the eminentia intercondylaris and in which the posterior cruciate ligament originates.
Area intercondylaris anterior
The anterior fossa, which borders the eminentia intercondylaris and in which the anterior cruciate ligament originates.
Facies articularis fibularis
The almost vertical lateral edge of the caput tibiae, which articulates with the fibular head caput fibulae.
Shank / Corpus tibiae
Pes anserinus
The pes anserinus (goosefoot) is an insertion area for four thigh muscles that attach to the tibia via the inner back of the knee. It is subdivided into superficial and deep:
Pes anserinus superficialis
the semitendinosus, gracilis and sartorius muscles attach in a confluent tendon to the superficial pes anserinus, about 5 cm distal to the joint space
Pes anserinus profundus
the tendon of the semimembranosus attaches to the profund pes anserinus
Tibial tuberosity
The extensive, slightly raised proximal-ventral bony roughening of the tibial shaft to which the patellar ligament attaches and to which the contraction force of the quadriceps is transmitted.
Distal end
Medial malleolus
The medial malleolus is the medial border of the talus , also known as the „medial malleolus“. In addition to this essentially vertical articular surface (facies articularis malleolaris), there is also the concave, approximately horizontal articular surface with which the tibia stands longitudinally on the articular roller of the talus: Facies articularis inferior.
Articular surface
Joints
Images
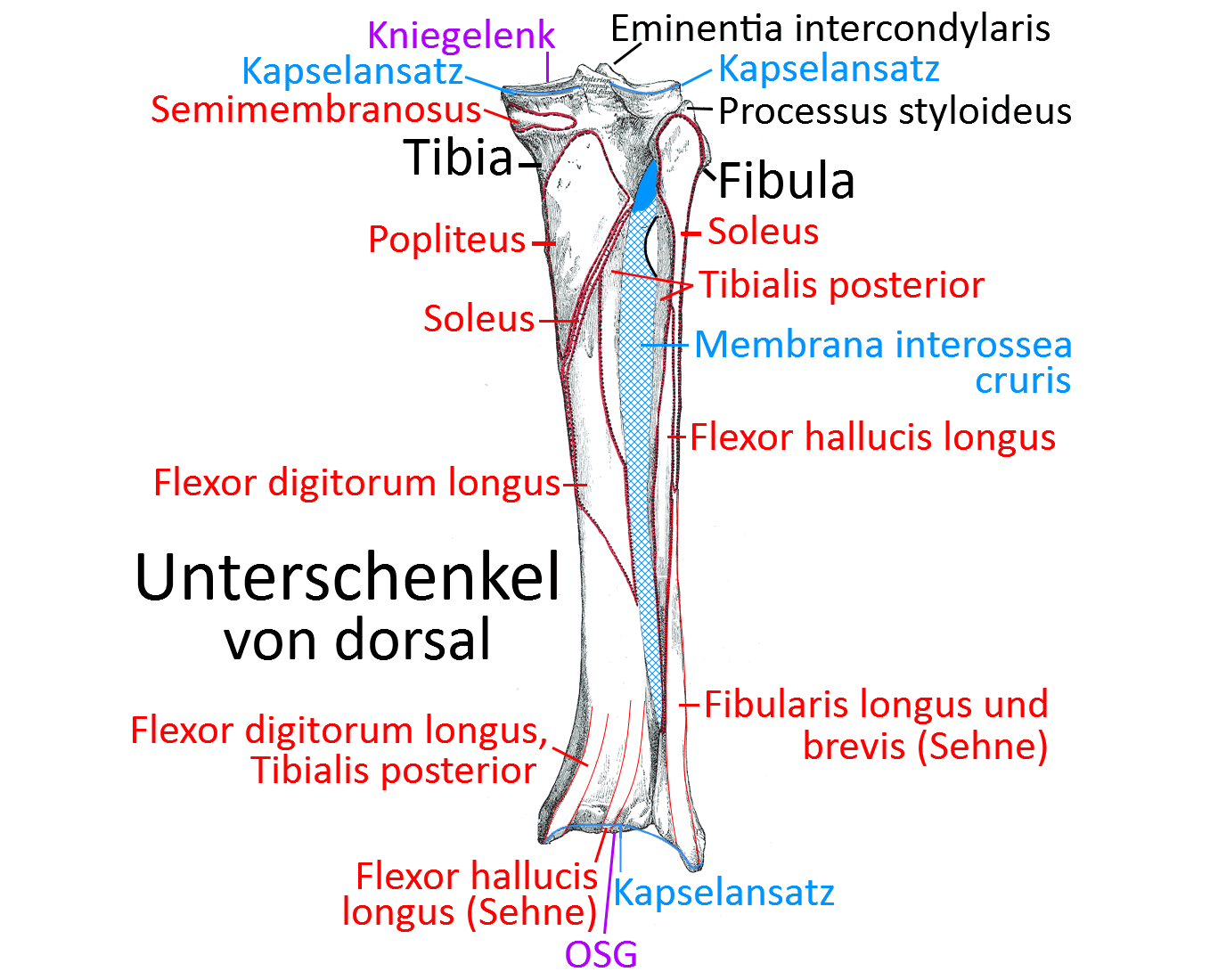
Tibia from dorsal view (image links to linkmap)
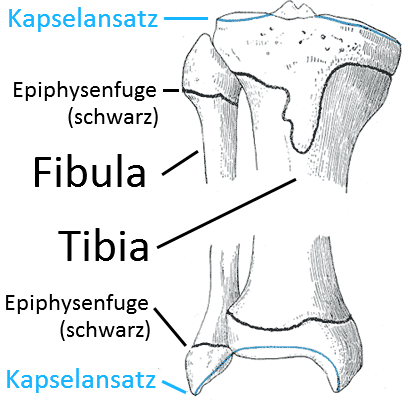
Epiphyseal plates