yogabook / muscles / subscapularis
Linkmap
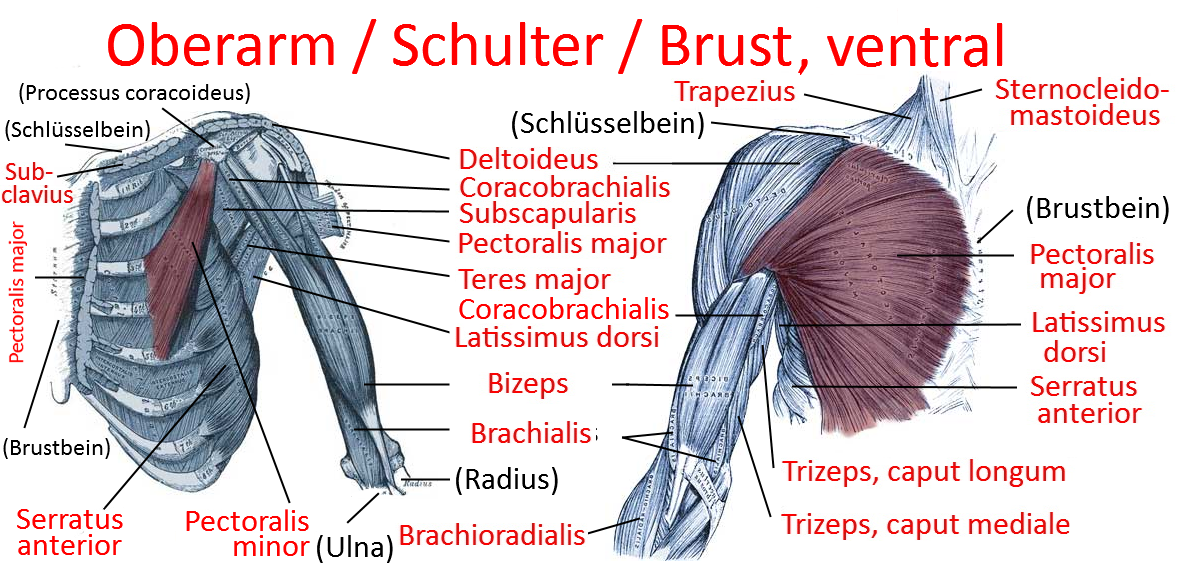
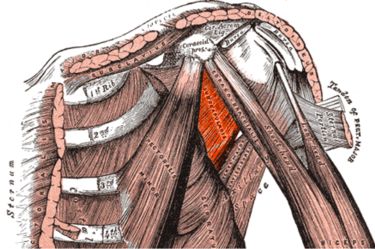
M. subscapularis
Scapulohumeral muscle of the shoulder girdle: the strongest internal rotator of the arm, originates on the front of the shoulder blade and attaches to the anterior upper humerus.
According to recent electromyographic studies, the cranial fibres of the subscapularis generate even greater torque than the supraspinatus between 0° and 60° lateral abduction. With increasing lateral abduction, the internally rotating effect of the subscapularis gradually weakens.
Origin: subscapular fossa(ventral surface of the scapula)
Attachment: Tuberculum minus of the humerus
Innervation: Nervi subscapulares, short motor branches from Fasciculus posterior of the plexus brachialis (C5-C7)
Antagonists:
Movement: internal rotation of the arm
Stretching postures (): Elbow stand, dog elbow stand, right-angled elbow stand, shoulder opening on the chair.
Tests
Lift-Off-Test, Belly-Press-Test
