yogabook / muscles / pectoralis major
Linkmap
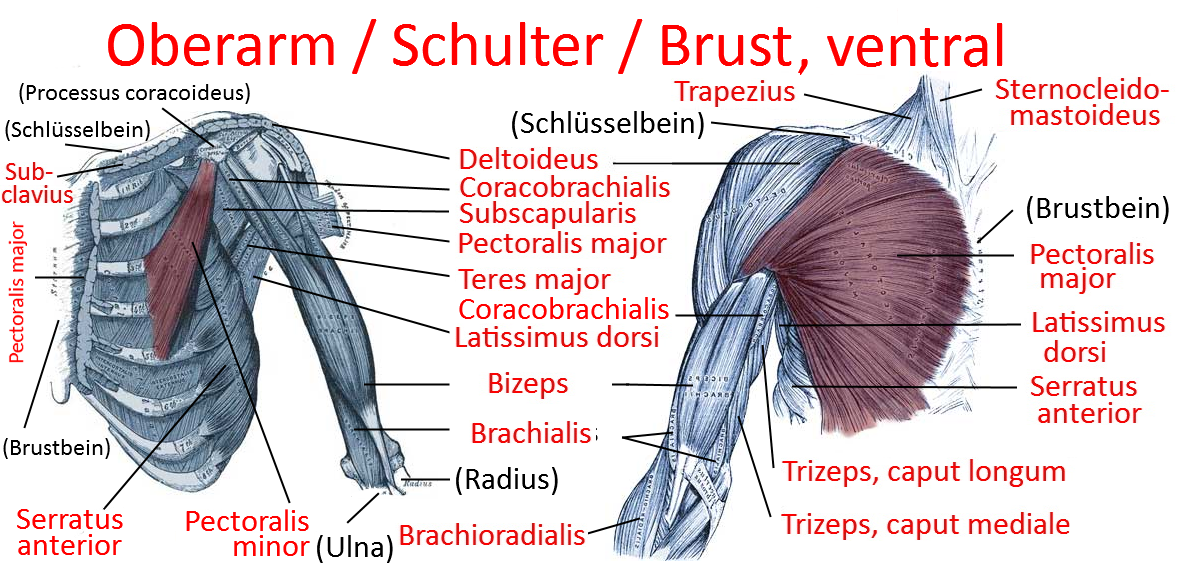
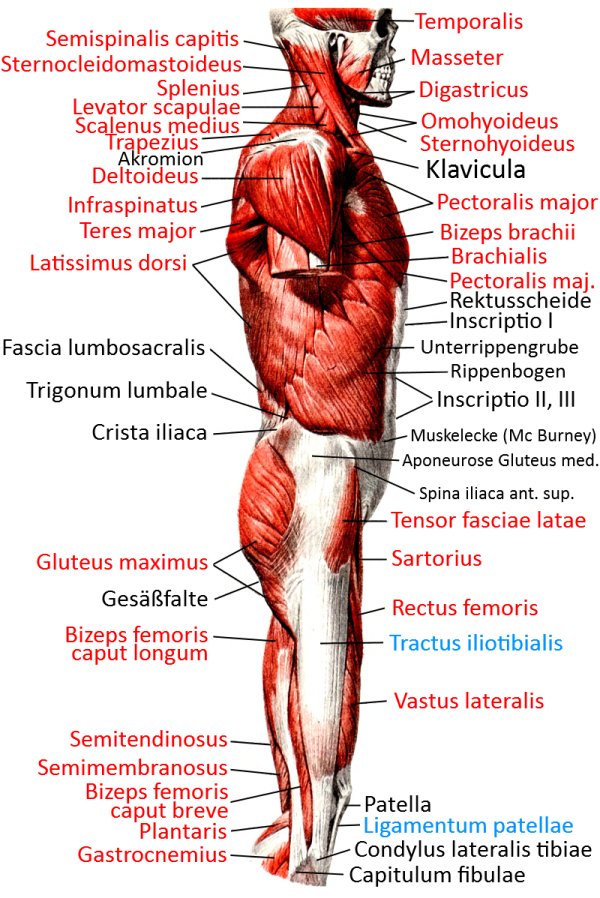
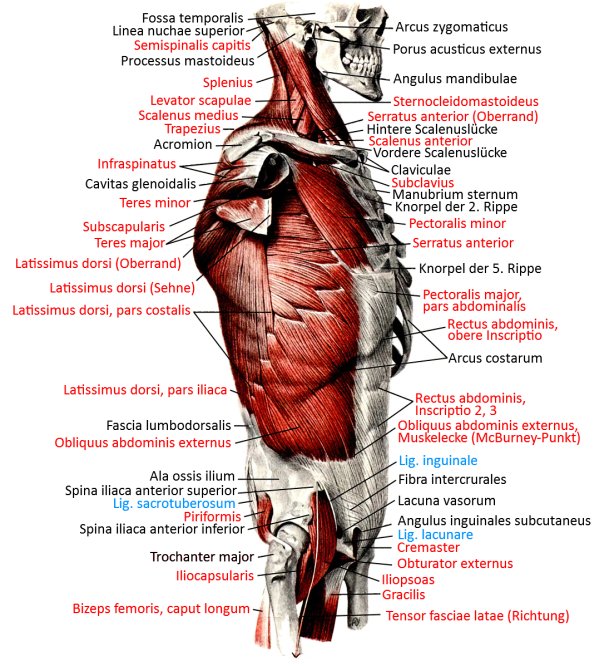
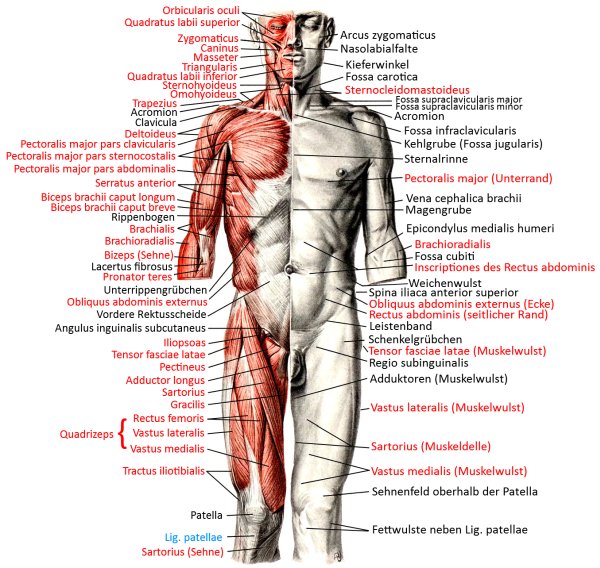
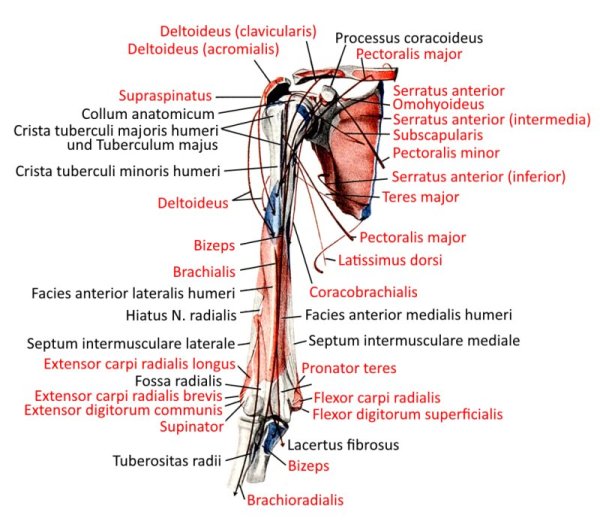
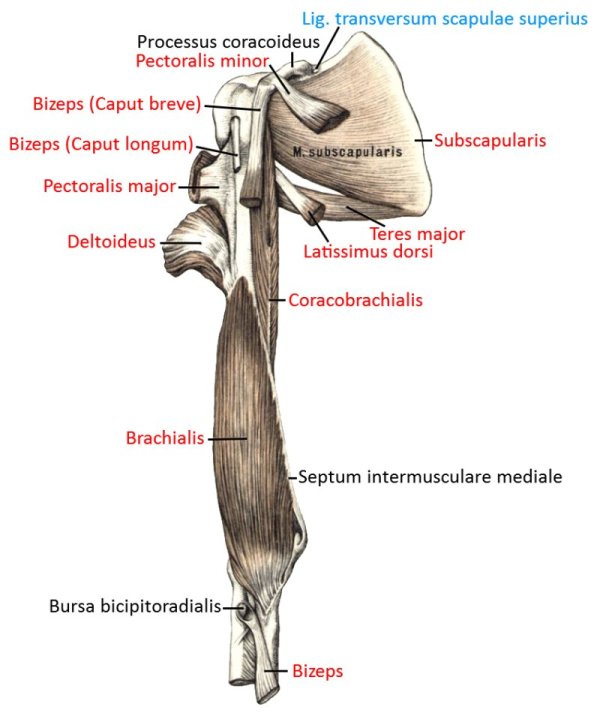
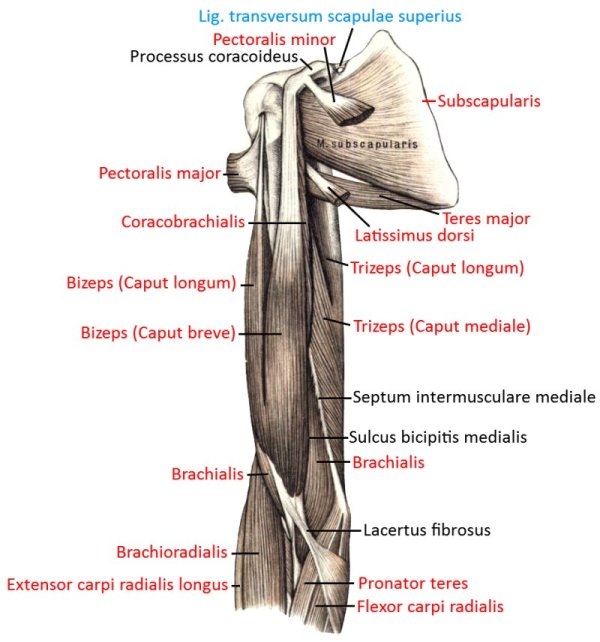
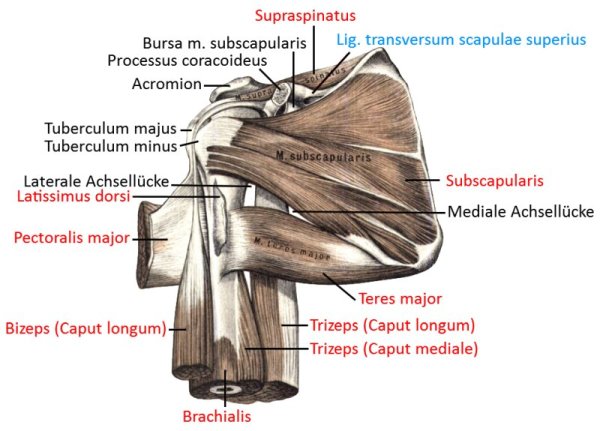
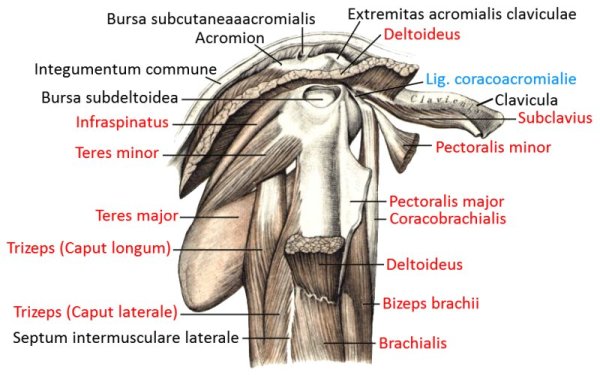
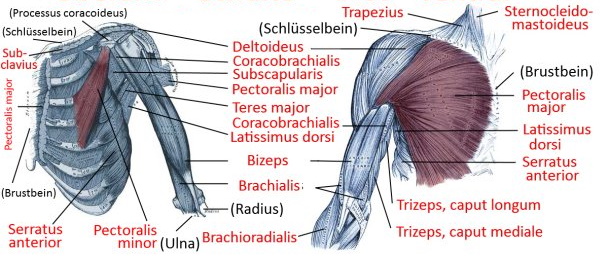
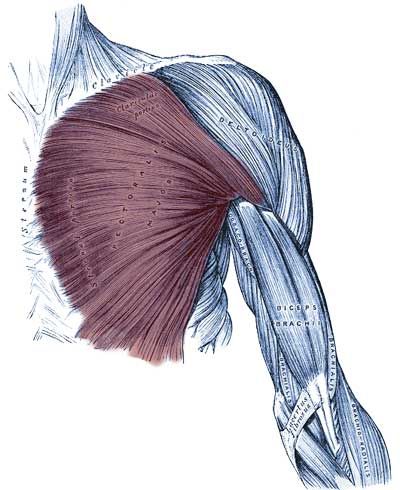
Pectoralis major
the three-headed large pectoral muscle, a truncohumeral muscle of the shoulder girdle:
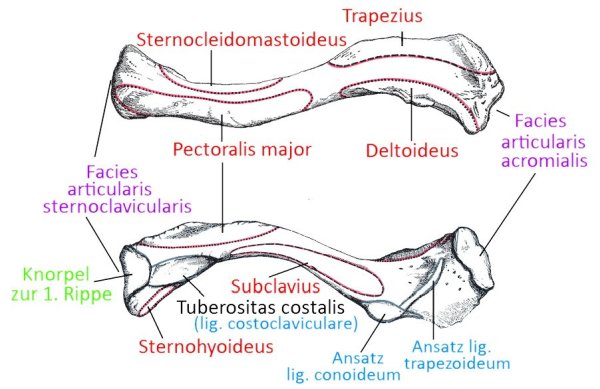
- pars clavicularis: originates from the medial half of the clavicle
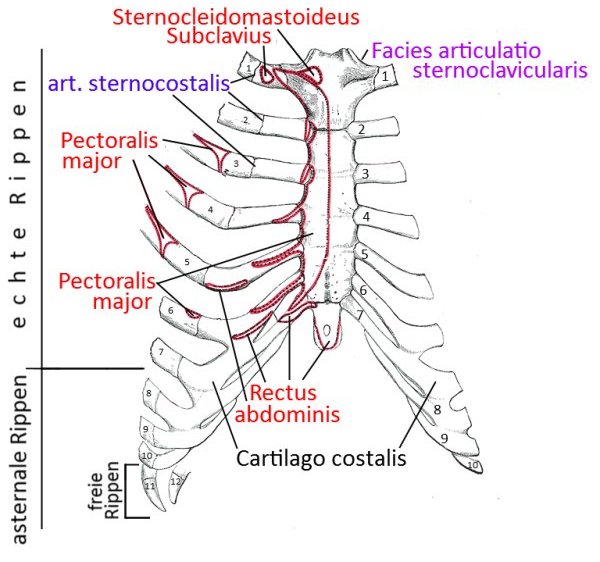
- pars sternocostalis: originates from the sternum and some rib cartilages
- pars abdominalis: originates at the uppermost area of the rectus sheath (the flat tendon structure made of tendons of the lateral abdominal muscles that envelops the rectus abdominis muscle ventrally and dorsally )
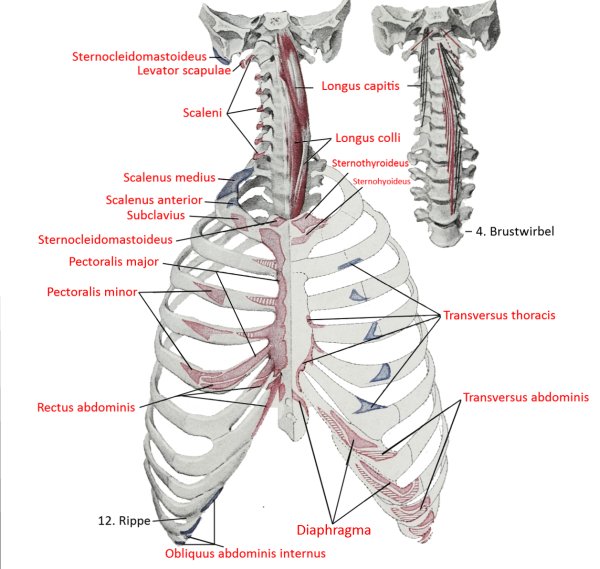
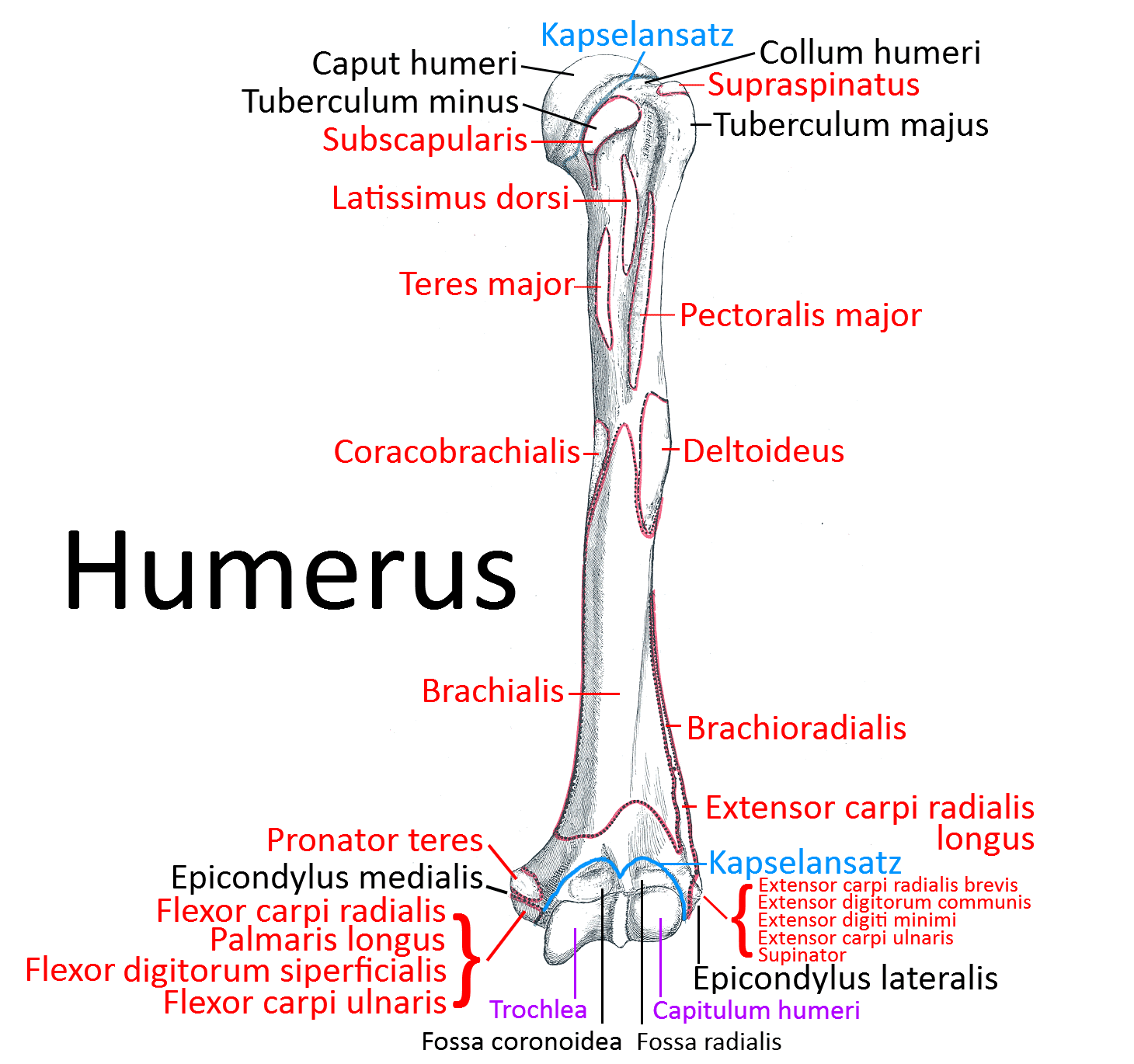
all parts adduct frontally and adduct laterally and can endorotate the arm. Pars sternocostalis and pars abdominalis can jointly lower the shoulder blade forwards. Pars clavicularis and pars sternocostalis can perform anteversion. The pectoralis major can act as an inspiratory respiratory support muscle when the arms are stationary. In addition to the pectoralis major, there is also the pectoralis minor, which, however, does not attach to the upper arm but to the shoulder blade in order to depress and protract it. More cranial fibers of the pectoralis major attach lower on the arm, more caudal fibers further up, which represents the muscle pull that limits the armpit to the front. If the arm is close to standard anatomical position, the cranial and caudal fiber parts are overturned; with further abduction, the overturning increasingly dissolves. Like the pectoralis minor, the pectoralis major is an inspiratory respiratory support muscle when the arm is supported because it then supports the cranial movement of the ribs.
Origin: Clavicle, sternum, cartilage of ribs 1-6
Insertion: Crista tuberculi majoris of the humerus
Innervation: Nervi pectorales medialis et lateralis from Plexus brachialis from C5 bis Th1
Antagonists:
Movement: lateral adduction, anteversion from retroversion to approx. anatomical zero, endorotation, frontal adduction to approx. standard anatomical position, inspiratory respiratory support muscle with the arm propped up, mediate protraction of the scapula
Strengthening postures (512): Bar, twisting pose: both variations, , , , tolasana.
Stretching postures (511): namaste: on the back, parsvottanasana, purvottanasana, shoulder stand, setu bandha sarvangasana, maricyasana 1, maricyasana 3, urdhva dhanurasana, hyperbola, back extension: elevated,
Weitere Karten: