yogabook / muscles / semimembranosus
Linkmap
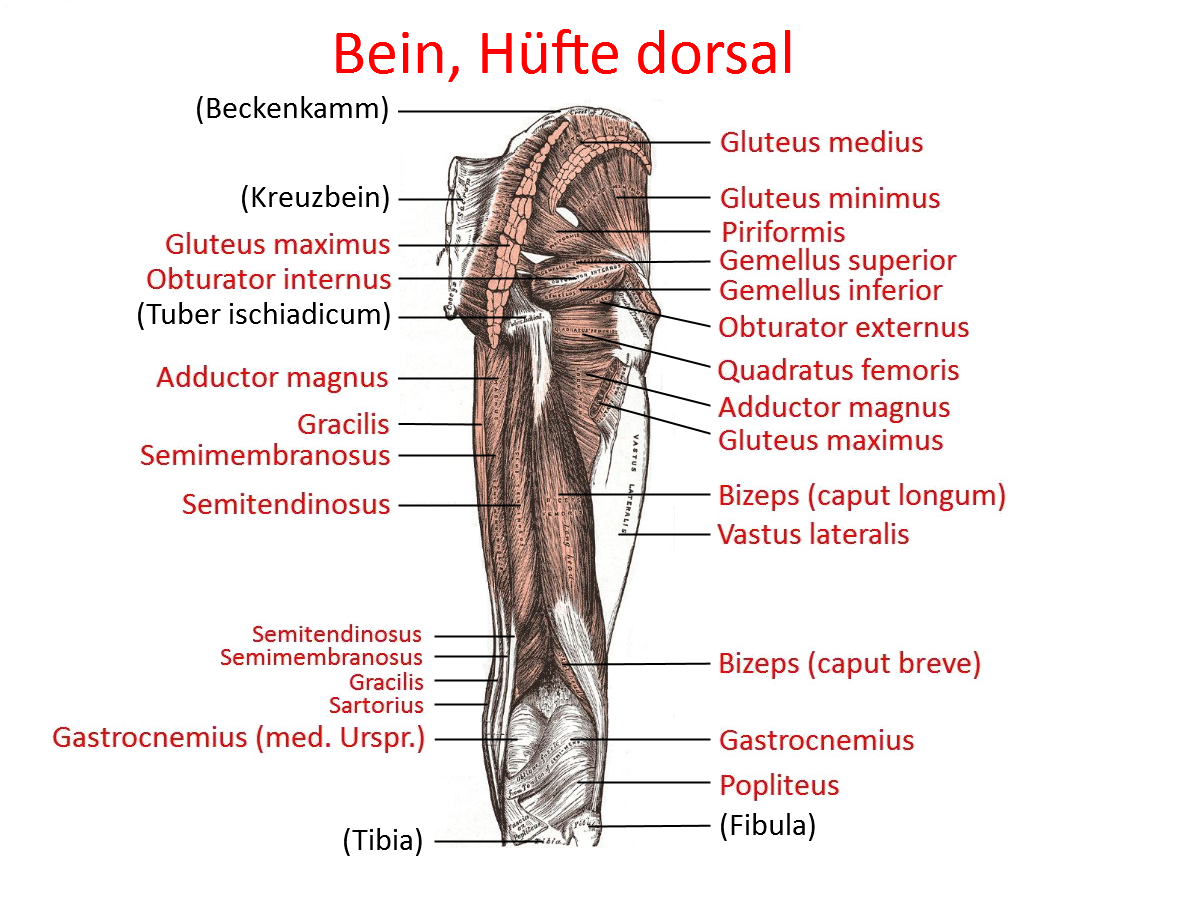
M. semimembranosus
originates at the lower posterior lateral ischium together with the caput longum of the leg biceps in a common head with the semitendinosus muscle. It has 5 fiber tracts at the base:
- Main fiber traction: attachment to the posterior and inner upper tibia bone
- Medial fiber traction: pulls to the dorsal capsule, to the POL and posterior horn of the medial meniscus
- Lateral fiber traction: to the lig. popliteum obliquum
- Fibers that run to the dorsal side of the medial tibial condyle
- caudal fiber tracts to the fascia of the popliteus and to the tibial periosteum(dorsal and dorsomedial surface)
With this complex approach, the semimembranosus is the determining factor in the stability of the dorsomedial joint corner of the knee joint.
It is involved in extension in the hip joint and flexes in the knee joint with simultaneous endorotation of the lower leg.
Origin: via a broad tendon of origin on the ischial tuberosity (ischial tuberosity)
Insertion: on the medial condyle of the tibia in the pes anserinus profundus, popliteum obliquum ligament, fascia of the popliteus
Innervation: N. tibialis (L5-S2)
Antagonists:
Movement: Extension in the hip joint, flexion of the knee joint, endorotation in the knee joint
Stretching poses (721): ardha baddha padma pascimottanasana, tryangamukhaikapada pscimottanasana, pascimottanasana, janu sirsasana, parivrtta janu sirsasana, parsva upavista konasana, upavista konasana: forward bend, parivrtta parsva upavista konasana, uttanasana, prasarita padottanasana, 3. Warrior pose, trikonasana, parivrtta trikonasana, ardha chandrasana, parivrtta ardha chandrasana, 5. Hip opening, handstand: eka pada, hanumanasana, hasta padangusthasana, downface dog, headstand: eka pada, krouncasana, supta krouncasana, parsvottanasana, right-angled handstand, right-angled elbowstand, back extension, shoulderstand: eka pada, supta konasana, supta padangusthasana, vasisthasana.htm, deadlift.
